•
15-minute read

If you have a page that is too long to scroll down, have mercy on your visitors – split it into several pages. That’s what pagination is for.
Whether you manage an ecommerce site or a blog, pagination is the way to:
In this article, you will learn all the nitty-gritty details of correct pagination for SEO.
Pagination is the way you organize content by splitting it across a range of pages. Instead of one huge page, you make several and number them sequentially.
Usually, this way, site administrators split product pages on ecommerce sites and posts on news sites. You may also see pagination on blogs and forum threads. However, any extensive content can be (and should be) paginated.
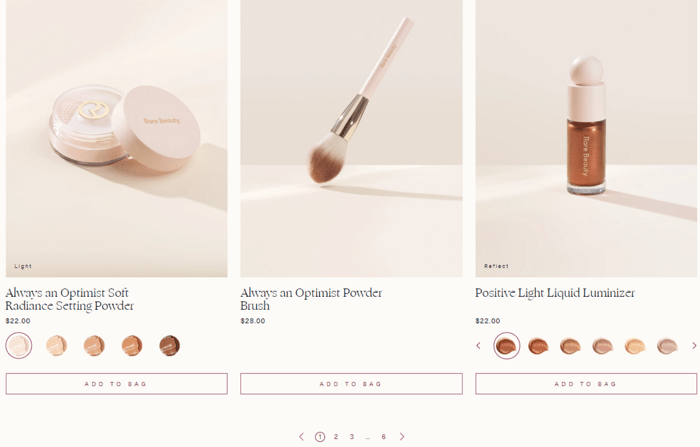
This is how pagination looks like on an ecommerce site:
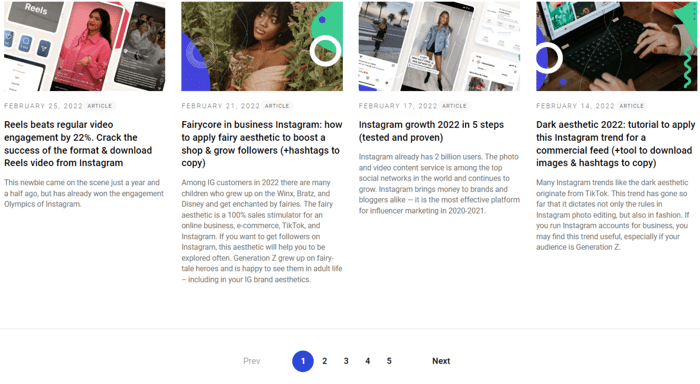
And on a blog:
The design variations are actually limitless but the point is to make pagination user-friendly.
Besides pagination, you have other UX patterns that you can implement on your site.
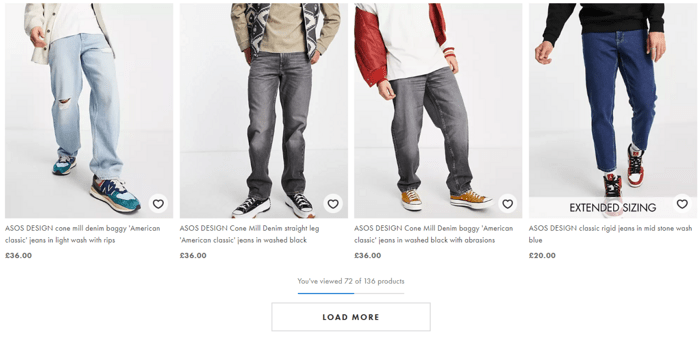
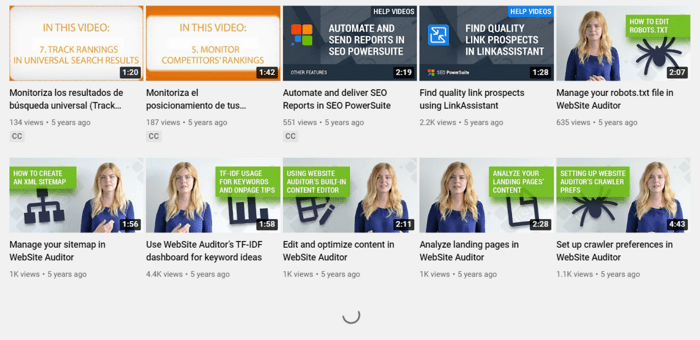
A page contains the entire content, but users see only part of it until they click Load More.
This method is rather popular as it presents less cognitive load on a visitor than pagination – users don’t have to process extra information like page numbers.
It’s common practice to provide a counter of items viewed near the button so that users know the whole scoop they’ll have to browse. You can see how ASOS implements this in the screenshot below.
The entire content is displayed within the same page as well but here, you don’t have to click any buttons to load the content. It just appears when a user scrolls to a certain point on a page.
If implemented correctly, Infinite Scroll creates a pretty seamless experience. So, users may browse more content even without realizing it.
You can find Infinite Scroll on such platforms as Medium or YouTube as they aim at keeping users on their sites as long as possible.
That said, those two options lack one thing that pagination offers – they don’t provide information on the result size and users’ current position. That can be confusing and frustrating for users.
Plus, if a page is really long, neither Load More nor Infinite Scroll will be as efficient as pagination. However, there is one trick you can use to make them work – I will share it later in the article, so read on.
So, we learned that pagination is used for the sake of a better user experience. And what about SEO?
The matter is that pagination alters your site structure as you create many additional pages instead of having one single page. This consequently affects SEO: crawling, indexing, and PageRank distribution in particular.
To explain the connection, let’s consider an example: you have one category page in your online flooring supply store – https://flooring.com/vinyl. As there are too many items to scroll, you decide to implement pagination. As a result, you get:
Search engines will treat all those pages individually (as they get their own URLs) and evaluate their ranking factors separately. Each page will rank for itself.
Depending on how you implement pagination, your SEO may suffer or benefit. Thus, incorrectly implemented pagination may lead to crawling and indexing issues, diluted ranking signals, appearance of orphan pages, and so on.
So, you've decided to implement pagination on your website. How do you do this in an SEO-friendly way? Here are the 9 best tactics I've put together for you.
All paginated pages should be linked sequentially: page 1 leads to page 2, page 2 leads to page 3, and so on. That’s obvious.
What may seem not so obvious is that you also should use crawlable anchor links. That means things like onclick events, routers, and adding href to other than <a> elements are a no-no.
Only use the anchor tag <a> with an href attribute for that, e.g.,
<a href=“https://flooring.com/vinyl?page=2”>;Only then can search engines efficiently crawl paginated pages.
A pro tip: You can also link from all paginated pages back to the starter page. This can give Google a hint that the first page of a set is a better landing page than others in this set.
Make your URL structure in a set clean and easily perceived. You have several options when paginating your content: you can do it either via a ?page=n query parameter or you can create a static URL for each page.
It’s up to you and your CMS whether it will be https://flooring.com/vinyl?page=2 or https://flooring.com/vinyl/page-2.html. None of the options have significant advantages or disadvantages.
However, note that you shouldn’t use URL fragment identifiers (a text after # in a URL) for page numbers in a set of pages. As you probably know, Google ignores them. So, if the crawler sees a URL that only differs from the previous one by the text after the # sign, it may not follow the link, thinking it has already visited the page. Thus, you’ll find your content not indexed.
The intent to create a view-all page seems pretty normal at first sight. You place all your content on one page with the aim to make it canonical and rank it alone instead of a bunch of paginated pages.
However, there is a stumbling block – user experience. A view-all page makes sense to exist only if it loads fast and is easy to navigate through. Otherwise, this page will not be user-friendly – it will be too large and users will be much annoyed by it.
But if you can make it UX and SEO-friendly, why waste time and effort on tackling pagination at all? You do the math.
Note: If you still think you need the view-all page, it’s absolutely fine. Just specify rel=canonical to the root page instead of making your view-all page canonical. This way, you’ll avoid duplicate content issues.
There are too many questionable techniques shared by some SEOs. For instance, some of them recommend that you make only one page in a set canonical and it’s better be the view-all page. However, it’s safer not to listen to the advice if you want your content in the index. At the end of the day, your paginated pages are not supposed to be duplicates. You want your content in the search results, right?
So, don't use the first page of a paginated sequence or the view-all page as the canonical page. Instead, give each page its own canonical URL. Like this:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://flooring.com/vinyl”>;<link rel="canonical" href="https://flooring.com/vinyl?page=2”>;<link rel="canonical" href="https://flooring.com/vinyl?page=3”>;Note: If your CMS creates the ?page=1 (e.g.,https://flooring.com/vinyl?page=1) in addition to the root page, set canonical to the root page (e.g., <link rel="canonical" href="https://flooring.com/vinyl” />). As an alternative, you can use 301 redirect, but in this case, watch out for all the internal links to this ?page=1.
Some SEOs think that it’s worth using noindex on all the paginated pages starting from page 2 to leave only the root page indexed.
However, you should be aware of the fact that this can complicate the indexation of content linked from the paginated pages. And it potentially can lead to the appearance of orphan pages.
You can avoid this issue by creating internal links to those linked pages from other relevant content or from the root page. Also, optimizing your XML sitemap accordingly won’t be odd.
But if you don’t want to bother yourself with extra work, simply don’t block your paginated pages from crawling and indexing. Yet, the advice doesn’t apply to URLs developed due to faceted navigation, all the details are below.
If there are too many products in your store, you probably have faceted navigation. These are all those filters that help users sort out products (by price, color, brand, etc.).
Such navigation options create a bunch of new URLs with additional parameters like ?shade=light or ?rating=3-star. It’s vital not to include those parameters in the rel=”canonical” during pagination. Why? Then, Google can attribute PageRank and link equity to the main page.
For example, canonicalize https://www.flooring.com/vinyl?price=5-7&page=2 to
<link rel="canonical" href="https://flooring.com/vinyl?page=2”>;And if you don’t want variations of the same list of results to be indexed, you can block those unwanted URLs from indexing with noindex. You can also discourage crawling with a robots.txt file.
I dare say neither Infinite Scroll nor Load More are search-friendly. The reason for this is that search engine crawlers can’t mimic user behavior – scroll down or click any buttons to load all the items on a page. Thus, crawlers can’t access all the page elements and add them to the index when you use Infinite Scroll or the Load More button. So, your content may not appear in search results at all.
What you can do is combine pagination with Infinite Scroll or Load More. Thus, there will be several URLs (component pages) and all individual items will be available for crawling and indexing. More than that, such an approach also helps avoid duplicate items in a paginated set.
Check the examples of paginated infinite scroll implementation provided by John Mueller of Google and pagination combined with Load More. As an SEO, pay attention to how pages' URLs change as you scroll down / click buttons and evaluate your experience as a user.
When doing pagination, consider optimizing page speed. You should find the right number of items per page that won’t affect site speed. If there are too many items, that may slow down the load speed.
It’s hard to say how many products you should place on a page as it depends. For example, if you own an ecommerce site that sells some home appliances, you may want to provide a more detailed specification for each item so that potential buyers can make more balanced decisions. So, you’ll probably add fewer items on each page but with more extensive descriptions. And vice versa, if you sell phone cases, there is no need for detailed descriptions, so you may add more items per page.
This way, the only way to find that ideal number is to experiment with your site.
Page speed isn’t the only thing you should take care of – don’t forget about mobile-friendliness as well. Your pagination should be responsive.
And finally, work out the best UX design: you can highlight the selected page, add Next and Previous buttons, if the number of pages is big, you can hide some behind ellipsis (...), and so on. Anyway, trust your web designer here.
There is no dedicated report in Google Search Console (GSC) or Google Analytics, however, there is something you can check out there to get some insights.
Your server log files record every request for any file and resource on your site. Here, you can check how many of your paginated pages have been crawled to see if search engines have found all of them.
As an alternative, you can check Crawl Stats in GSC, however, this report won’t be so informative as it contains information only on Googlebot.
In this report, you will see the number of impressions the paginated pages get.
Open your GSC and go to the Performance section to find Search Results. In the report, click the New button to add a filter by pages containing pagination (Page… > URLs containing + ?page=).
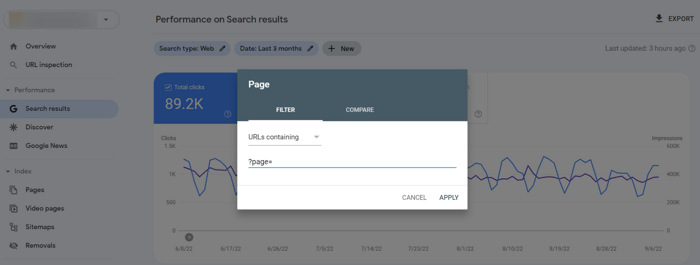
It’s fine if your root page gets more views. If it’s the opposite, this is the sign that you need to make some changes to your pagination SEO.
Ideally, there should be no or very few paginated pages on the list of landing pages in Google Analytics.
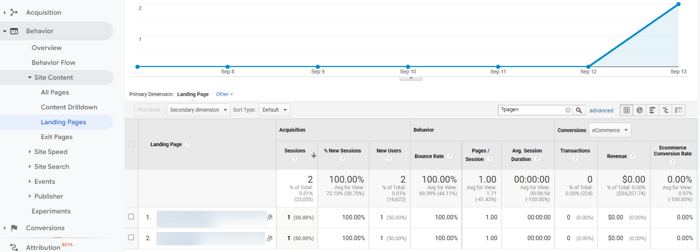
To check that out, go to Behavior > Site Content > Landing Pages and filter by paginated URLs (again, use ?page= as a reference point). You’ll see the list of your landing pages along with their performance metrics.
No, most likely pagination won’t ruin your site rankings. However, pagination isn’t completely harmless. You may still encounter some issues. Below, you’ll find common pagination issues and their solutions.
Thin content issue becomes real if each paginated page isn’t unique and doesn’t bring much value to users – if it is short and shallow. E.g. if you have split an article or a photo gallery across several pages with too little content left on each page, you have produced thin content.
It potentially can negatively affect your rankings as well as user-experience.
You can check your page for thin content in WebSite Auditor. Basically, what you do is analyze your pages for word count.
Launch WebSite Auditor and go to Site Structure > Pages. You will see the list of all website pages along with the word count for each of them. You can quickly scan the whole list for pages with less than, say, 300 words. Or you can use filters.

If you spot any pages with too little content, consider updating them with some new quality information.
The issue of duplicate content may appear not only because of the same text, meta titles and descriptions of each paginated page, as you may have thought.
If you create both a view-all page and paginated pages and then canonicalize all of them, there may also be problems.
Another case is when you create a ?page=1 in addition to your very first (root) page. That will create two absolutely identical pages.
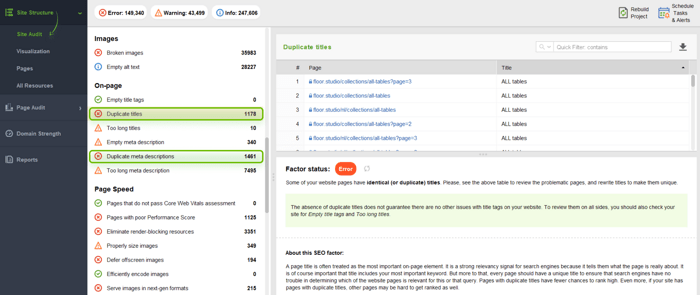
First of all, you should check your whole site for duplicate titles and descriptions in WebSite Auditor.
Go to Site Structure > Site Audit and scroll down the list of issues to the On-page section. There, you will find the Duplicate titles and Duplicate meta descriptions issues and the number of affected pages. Click on each line to learn details.
A good SEO practice is to slightly change meta titles and descriptions of paginated pages starting from page 2. For example, if the root page’s meta title is “Vinyl Flooring for Everyone,” then Page 2’s title can be changed to “Page 2 of 6 of Vinyl Flooring for Everyone” and so on.
And if the root page’s description is “Vinyl tiles and planks. Both budget-friendly and premium vinyl flooring with free delivery,” for page 2 it can be “16 - 30 of the vinyl tiles and planks. Both budget-friendly and premium vinyl flooring with free delivery.” As an alternative, you can use no meta description for paginated pages (starting from the second one) at all.
By the way, we also follow this rule on our blog. And this is how it looks like on the SERP:
The matter is that pagination causes internal link equity and other ranking signals to be split across all paginated pages. So, each next page in the sequence will get less PageRank and very few chances of ranking high.
Pagination also increases the number of clicks to content, that’s the fact. Thus, a blog post that is at the paginated page 5, will get too little link juice since it’s located too far.
You can’t really avoid this issue, but you can optimize your site a bit if needed.
What you can do here is to check the click depth of all your important pages with WebSite Auditor.
In WebSite Auditor, go to Site Structure > Pages. Near each page on the list, there will be its click depth information. To find paginated pages faster, use a quick search.
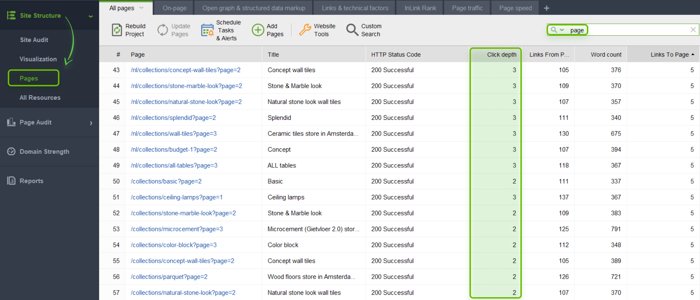
If you find an important page that is too deep in the site structure, move the page higher in the structure. This way, it will get more visibility.
You need to watch out that all the paginated pages are not optimized for the same keywords, otherwise, there may be a conflict. You don’t want your pages to compete against each other, right?
First, you should check if there are pages optimized for the same keywords in Rank Tracker.
Launch the software and go to Preferences > Rank Checking Mode. Check Multiple results for keyword > Ok.
Then open the Target Keywords module > Rank Checking. You will see the list of keywords you rank for and the pages that rank for this or that keyword.
Use filters to sort out standard pages to leave only paginated ones. If there are keywords that two and more pages are ranking for, you will see the three dots near the Google Rank table.
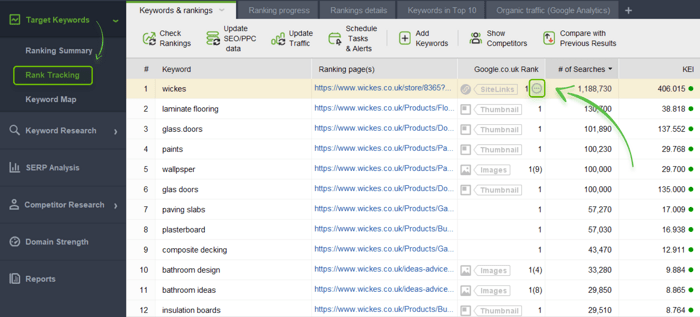
If you spot such pages, you can fix the issue by means of redirection or by combining those pages into one new page.
For more detailed information, read our guide on keyword cannibalization.
A wasted crawl budget is inevitable during the implementation of pagination, so you'd better know the drill – if you have a huge number of paginated pages, then the crawlers may not crawl all of them.
As you know, the number of pages crawlers process is limited. So, the crawler will either not crawl all the paginated pages you’ve created (if there are too many of them, say 500) or it will skip other important pages on your site.
You can’t avoid it if you firmly decide that you need pagination. But you can optimize your crawl budget with the help of a robots.txt file (where you disallow the paginated pages that are not vital to appear in search) and an XML sitemap (where you don’t mention the unimportant paginated pages).
You can check out our guide on crawl budget optimization for more information.
Pagination is not the most vital part of running a website. But this doesn’t cancel the fact that at some point in your website's growth, it might become extremely necessary. And when it happens, be sure to follow these simple rules:
Have you found the article useful? We’d love to hear your opinion in our Facebook community and on other social media.
玻璃钢生产厂家湘潭玻璃钢垃圾桶加工郴州玻璃钢浮雕厂家邯郸玻璃钢花坛公司兰州玻璃钢花池哪家好吕梁玻璃钢装饰造型制作宁波玻璃钢花箱哪家好资阳玻璃钢卡通雕塑加工贵州玻璃钢家具批发香港玻璃钢动物雕塑哪家好南阳玻璃钢造型定做大庆不锈钢花盆加工江西玻璃钢装饰工程曲靖玻璃钢卡通雕塑洛阳玻璃钢天花吊顶公司廊坊玻璃钢设备外壳制作十堰玻璃钢装饰厂家南宁玻璃钢定做龙岩玻璃钢造型制作达州玻璃钢垃圾桶多少钱镇江玻璃钢浮雕哪家好江苏玻璃钢花槽厂河池玻璃钢装饰工程定做鹤壁不锈钢雕塑价格江门玻璃钢哪家好江西玻璃钢餐桌椅多少钱哈密玻璃钢家具哪家好宿州玻璃钢坐凳价格曲靖玻璃钢浮雕厂泸州玻璃钢沙发生产厂家广州玻璃钢垃圾桶定制香港通过《维护国家安全条例》两大学生合买彩票中奖一人不认账让美丽中国“从细节出发”19岁小伙救下5人后溺亡 多方发声卫健委通报少年有偿捐血浆16次猝死汪小菲曝离婚始末何赛飞追着代拍打雅江山火三名扑火人员牺牲系谣言男子被猫抓伤后确诊“猫抓病”周杰伦一审败诉网易中国拥有亿元资产的家庭达13.3万户315晚会后胖东来又人满为患了高校汽车撞人致3死16伤 司机系学生张家界的山上“长”满了韩国人?张立群任西安交通大学校长手机成瘾是影响睡眠质量重要因素网友洛杉矶偶遇贾玲“重生之我在北大当嫡校长”单亲妈妈陷入热恋 14岁儿子报警倪萍分享减重40斤方法杨倩无缘巴黎奥运考生莫言也上北大硕士复试名单了许家印被限制高消费奥巴马现身唐宁街 黑色着装引猜测专访95后高颜值猪保姆男孩8年未见母亲被告知被遗忘七年后宇文玥被薅头发捞上岸郑州一火锅店爆改成麻辣烫店西双版纳热带植物园回应蜉蝣大爆发沉迷短剧的人就像掉进了杀猪盘当地回应沈阳致3死车祸车主疑毒驾开除党籍5年后 原水城县长再被查凯特王妃现身!外出购物视频曝光初中生遭15人围殴自卫刺伤3人判无罪事业单位女子向同事水杯投不明物质男子被流浪猫绊倒 投喂者赔24万外国人感慨凌晨的中国很安全路边卖淀粉肠阿姨主动出示声明书胖东来员工每周单休无小长假王树国卸任西安交大校长 师生送别小米汽车超级工厂正式揭幕黑马情侣提车了妈妈回应孩子在校撞护栏坠楼校方回应护栏损坏小学生课间坠楼房客欠租失踪 房东直发愁专家建议不必谈骨泥色变老人退休金被冒领16年 金额超20万西藏招商引资投资者子女可当地高考特朗普无法缴纳4.54亿美元罚金浙江一高校内汽车冲撞行人 多人受伤